If you work in Digital Marketing, or even if you don’t… you are probably aware of the huge impact that search engine ranking has on the performance of a website.
If your customers are searching for something, the chances are, unless they’re looking for something incredibly specific, they’re going to click on one of the top three-or-so results that google presents them with. Even if they’re still undecided, the chances of them venturing into the second page are slim, with studies show that only 9.90% of mobile users and 7.60% of desktop users ever click on the second page of google results.
With that in mind, ranking on the first page of a search engine’s results is hugely important to your website’s success. This is where SEO comes in.
What is SEO?
SEO, an abbreviation of Search Engine Optimisation, is the process of tailoring a piece of content or a website, to organically increase its Google, or other search engine ranking. Simply put, if your page has a good SEO ranking, it will appear higher on a search engine results page (SERP). Whereas a poorly optimised page will appear lower down, generating less traffic.
How Do Search Engines Work?
One of the main themes surrounding SEO is relevance. Search engines, at the end of the day, are businesses. Google, Bing, Yahoo they are all competing for your searches, and to do that they need to provide the most relevant results to keep you coming back.
Search engines aren’t magic, and they don’t innately know what websites exist on the Internet. To give their visitors the best, most accurate results, search engines send out ‘crawlers’ to scour the web. These crawlers move across the web, from link to link, assessing the content on each and every page they come across and storing it in a database. Then, when a term is searched, a search engine looks over this database and pulls out the most relevant sites to your search query.
For example, say you go to Google and search “Houseplants UK”. Google will jump straight into its database and pull out the websites it feels are the most relevant to your search, based on what the crawler has found.
Despite their creepy-crawly name, web crawlers are definitely not something to be afraid of. In fact, good SEO practice means making your page as welcoming and accessible to crawlers as possible! This means including subject-relevant keywords in your page’s:
- Meta Description
- Title
- Headers
- URL
- Body Content
- Image ‘Alt Attributes’
We’ll go into these further later on.
White Hat vs Black Hat SEO
 The majority of SEO strategies is split up into two categories; White Hat and Black Hat.‘White Hat’ refers to good-natured, people focused SEO techniques. These techniques focus on providing value and high-quality content to users through authentic, friendly optimisation.
The majority of SEO strategies is split up into two categories; White Hat and Black Hat.‘White Hat’ refers to good-natured, people focused SEO techniques. These techniques focus on providing value and high-quality content to users through authentic, friendly optimisation.
White hat strategies include:
- Producing relevant, high quality content
- Writing well-optimised, readable and grammatically correct content
- Including keyword-rich crawlable assets
- Keeping loading speeds down
- Securing back-links from relevant, trustworthy websites
On the other hand, ‘Black Hat’ refers to shady, underhanded SEO tactics. These tactics focus on tricking search engines into ranking them highly.
Black hat strategies include:
- Invisible keywords
- Keyword ‘stuffing’
- Irrelevant links
- Purchased links
- Cloaking
Black hat SEO, while still prevalent, is a dying practice. Web crawlers have come a long way in the past decade, and are now able to spot many common black hat tactics. This development means that black hat tactics are now extremely risky, as Google has been known to permanently ‘blacklist’ websites caught using these techniques. It is for that reason that we would never recommend our clients to use black hat tactics on their site.
How do I Improve my SEO ranking?
Now that you know the general law of the SEO land, let’s go into a few ways you that can build your SEO and rise up the results pages.
1. Keyword Research
Keyword research is one of the most important facets of an effective SEO strategy. By finding the right keyword, and optimising your content towards it, you can massively improve your search engine ranking. The best way to start this is by thinking about the words and phrases that define your business, its products/services, and its value proposition.
Let’s go back to the houseplant business we searched for earlier. A base keyword list for this business might look something like this.
- Houseplants
- Office Plants
- Plants
- Greenery
- Foliage
- Botanicals
These keywords are a great starting point, but statistically, the shorter and more popular a keyword/phrase is, the harder it is to rank for. So unless you have a long-standing website with spot-on sitewide SEO and a high user base, it’s better to specialise your keywords a little.
For example, ‘Houseplants’ is searched an average of 74,000 times every month. Narrowing that down a little bit, Houseplants UK is searched 18,100 times per month. Going even further, Houseplants Online UK has 1,600 monthly searches. These lower-volume keywords are also known as ‘long tail keywords’. You might think focusing on these keywords would be counter-productive, but if you’re looking for conversions, these are your golden ticket!
Someone who’s searching for ‘Houseplants’ could be looking for anything… Photos of houseplants, blogs about houseplants, the Wikipedia page on houseplants. Where someone searching for ‘Houseplants Online UK’ is most likely looking to buy houseplants, on the internet, from the UK. If that’s what you’re selling, and that’s what you’re ranking for, the money is in the bag.
On-page SEO Optimisation
Once you have your keywords, you’ll want to start using them to boost your SEO. To do that, you need to include them in your page’s crawlable assets. But be careful, keywords are a great, powerful SEO tool, however, if you overuse keywords in your page, you can be flagged for ‘keyword stuffing’, which can damage your SEO ranking.
In other words…

Title Tags
The first chance your audience, and crawlers, get to see your keyword is in your page’s Title Tag. Your title tag is an HTML element that tells google and external link viewers what your page is about. Consider using keywords at the front-end of your titles to make it easier for users to see.
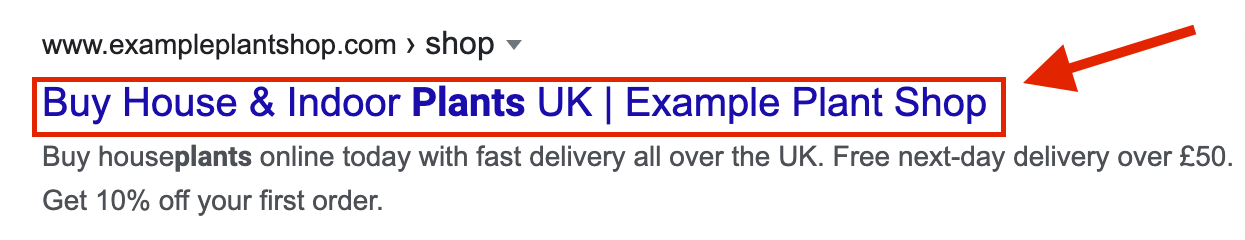
Not only can Title Tags boost your SEO Ranking, but they can also increase your post’s click-through rate on social media.

Meta Description
The next place that crawlers will look for keywords is in your Meta Description. The purpose of a meta description is to tell users (and search engines) exactly what’s on your page.
Meta descriptions allow for a little more depth than title tags, so you can paint a fuller picture of what users can expect from your page. But remember not to ramble, 150-300 characters is the sweet spot, and less is usually better than more!
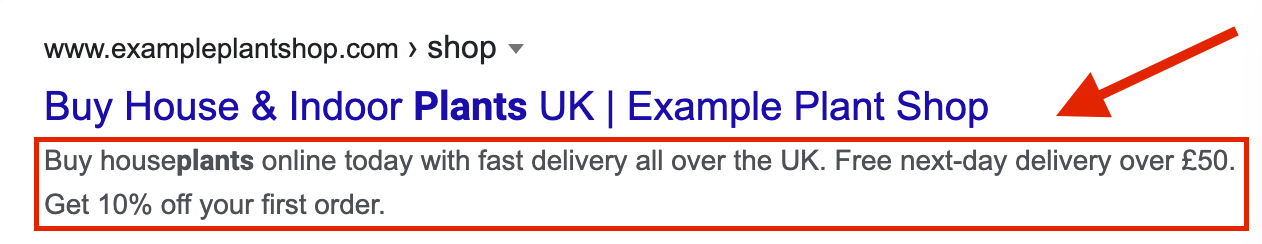
Header Tags (? Like this)
Next up are your Header tags. As you can imagine, these are your page titles, subtitles and other headers. By including keywords in this section, not only are you telling your audience what they’re looking at, but you’re telling crawlers that the content on your page is relevant to the keyword it’s ranking for.
Headers are numerically ranked in terms of importance, from:
- H1 (Main Title Tag)
- H2(Subheading)
- H3 (Sub-Subheading)
- H2(Subheading)
And so on…
The lower the H number, the more importance it will have over your SEO.
URL
You probably know what a URL is, but did you know that it can be a key weapon in your SEO arsenal? By including keywords in your URL, you can boost your webpage’s search visibility.
Just remember to keep it concise and readable.
It’s also worth keeping an eye on your URL trail, as several keyword-optimised page titles can lead to an ugly, keyword-stuffed URL. So if your URL looks something like:
https://exampleplantshop.com/blog/plants/houseplants/houseplant-advice/what-is-the-best-house-plant-for-my-house/
Google might flag this as potential spam due to the overuse of keywords. Instead, try removing the subfolders, now you’re left with:
https://exampleplantshop.com/blog/what-is-the-best-house-plant-for-my-house
Much better!
Image Alt Text
Alt Text (short for alternative text) refers to the part of an image’s HTML code that describes the appearance and function of the image. This can help your site in a number of ways:
1. By including image alt text, you provide crawlers with better image descriptions/context helping them to know exactly what an image shows. By properly optimising your alt text, you can boost your chances of landing in the top row of Google’s image search.
2. If your image doesn’t load, alt text will be displayed in its place, lowering the risk of page bounces.
3. By including alt text your site will be massively more accessible to sight-impaired website users. It’s the 21st century… you wouldn’t design a building without an accessible ramp. You wouldn’t build a car park without a disabled parking bay. Your website should be no different.
While your alt text should be keyword-optimised, it should also be descriptive and understandable. It also helps to change your image names to be SEO friendly too.
For example:
<src=”img_397493″ alt=”plant, houseplant, potted plant, leaf”>
Is a bad example of alt text. The image subject, while obvious, is not descriptive. This may also get flagged as spam on google due to the overuse of keywords in the text.
On the other hand,
<src=”philodendron scadens” alt=”Philodendron Scadens houseplant in a ceramic pot on a windowsill”>
Is much better. The text is descriptive and keyword-rich and describes the image to both users and search engines.
When writing your alt text, a good tip is to load up a text-to-speech generator, close your eyes and listen to the description. If you can paint a pretty good picture of the image in your head from your alt text, it should be pretty good.
2. Body Content
In the words of Bill Gates, “Content is King”. And this rings true with SEO. Your content is the key to successful SEO. Enticing title tags and optimised meta descriptions are all well and good, but in order to keep bounce rates down and ensure return visitors, your content must be engaging, well written and appropriate for your intended audience.
If you know you want to write about a topic, but you’re not sure what angle to take, try Answer The Public. All you need to do is enter your keyword, and the website will return hundreds of commonly searched questions, propositions and comparisons. It’s almost too easy.

We’re not here to teach you how to write a blog (yet…), but to if we had to give one piece of advice, it would be this: Before you start writing, ask yourself, is the content I’m about to write going to be interesting for my audience to read?
The answer should always be – yes, absolutely (in a really enthusiastic tone!).
Creating relevant content that brings value to your customers, focused around your keyword, is the most important step to secure those page-one results!
While you need to pay a certain amount of attention to keywords in the body of your text, this is the least of your content worries. Remember, you’re not just writing content to rank in Google, you’re actually writing it to build relationships with customers, increase awareness of your brand, and position your own business as industry experts.
3. Optimise your site
People often neglect the technical side of SEO. But how your website is built is extremely important to the SERP ranking of your site. You can have a beautiful site, with engaging, well-written content. But if your site’s technical SEO is lacking, you’re never going to rank.
Tags
If a site isn’t built properly, Google won’t be able to ‘crawl’ the page content for the information it needs to display it in search results. For example, if you just make your title bigger and bolder, and don’t actually use H1 tags, web crawlers can’t tell that it is a title. The same goes for H2, H3, H4 and so on…
Structure
Another technical SEO problem lies in ‘orphan’ pages and bad site structure. Remember how we said that crawlers move across the web link-to-link? This means that they can only find a page on your site if it is linked to somewhere else. And if a crawler can’t find your page, it’s not going to rank.
An easy way to identify orphan pages is by looking at your site’s least visited pages on Google Analytics. As orphan pages are incredibly difficult to find, they will likely have had next to no visitors. Once located, make sure to re-join it to your site through internal links.
Speed
The last website optimisation factor that can massively impact your SERP ranking is your site’s loading speed. According to research from Google, bounce rates increase by 32% when a page load time increases from 1 to 3 seconds. When this is increased to 5 seconds, the bounce rate increases by 90%! So you can see why loading speed is important!
Not only does it increase bounce rates, it directly impacts your page’s SERP ranking. Google first started considering site speed in their rankings way back in 2010, so there’s no excuse to ignore it!
Things like compressing large image files, optimising your code, and reducing redirects can all have huge impacts on your loading speed. If you’re not sure what improvements your site needs, Google’s official PageSpeed Insights tool is the best place to start. This is one of the tools that Google uses to assess your speed, so if you can get into the green on this, that’s great for your site!
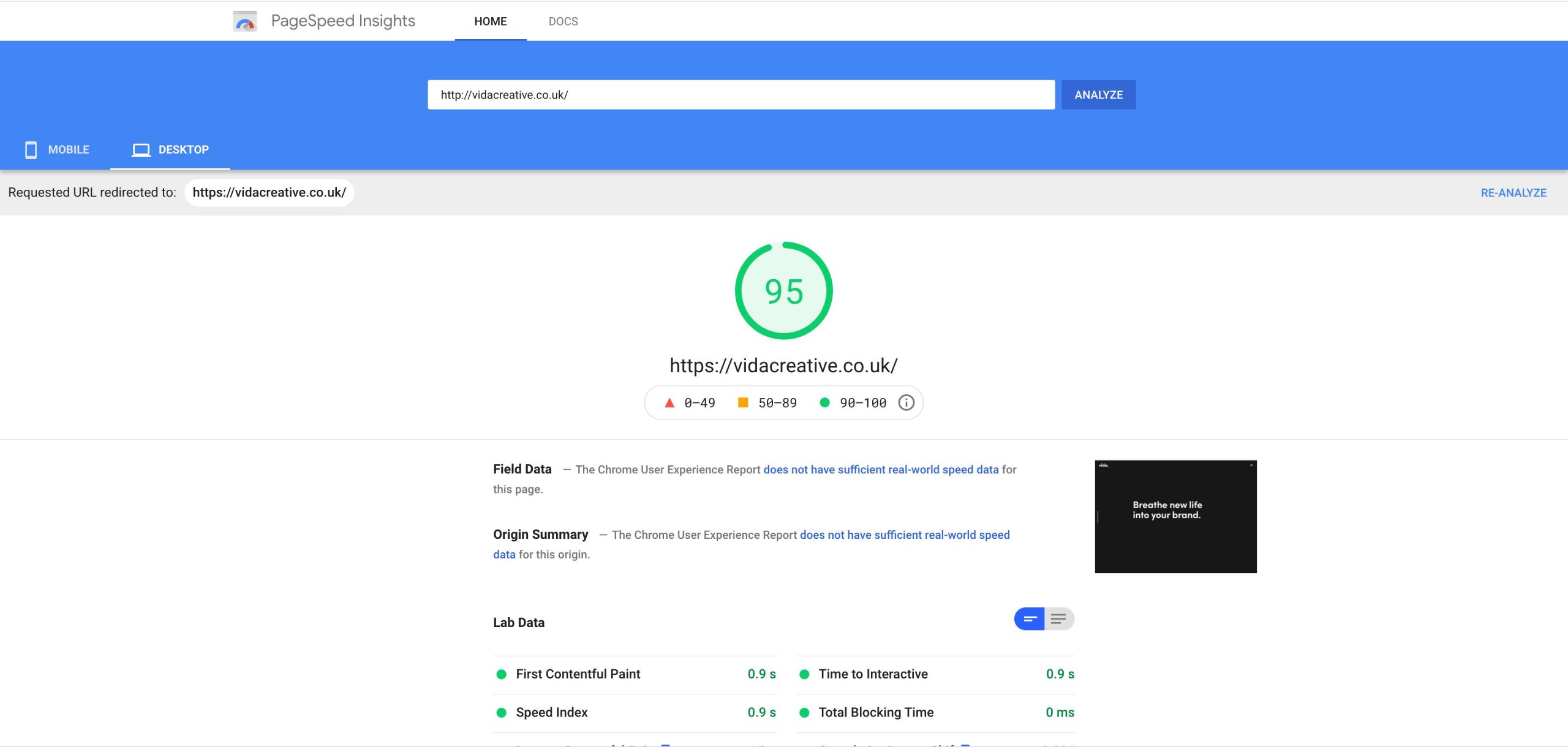
4. Build your Backlinks
We’ve already explained how crawlers move from link to link across the web. But what’s better than internal links? Backlinks! More specifically, backlinks from well-reputed, trustworthy websites. These kinds of sites are known as having high ‘domain authority’. Web crawlers crawl these bigger websites way more often than smaller sites, as they likely have multiple incoming links from all across the web. If you can secure a link from one of these sites, crawlers will see your site as more important.
Think of the internet like a school. These trustworthy websites are the ‘cool kids’, backlinks are respect, and your SERP ranking is your popularity. You’ll probably start school as a nobody, but if you get respect from the cool kids, your popularity will skyrocket. The more this happens, the more popular you get, and eventually, you’ll get to sit at the cool kids’ table (SERP first page).
Get it..?
Content, Content, Content
The best way to ensure backlinks is simply to create something worth sharing. In-depth blogs, detailed infographics, insightful videos, find out what people want to see and make it. However, even with a quality linkable asset, a smaller site will probably struggle to get quality links. But don’t give up! There are multiple ways (both black and white hat) to secure links on your site.
Broken Links
Perhaps the easiest method is through “broken link building”. This process involves researching articles describing the topic you want a link for and finding 404 errors within the links on the page.
For example, say you recently wrote a blog on “Top 5 tips for keeping your houseplants alive”. You would look on google for high-ranking, high authority resource pages on this topic. Something like this.
From there, check on the links on this page, and with any luck, you’ll find a broken link to a 404 error. If not, move on and try again. But if you do, now is your time to strike! Find the site owner’s details, and send them a friendly email notifying them of the broken link, and suggesting that you have a great alternative blog that they could link to instead.
Blog owners don’t want broken links on their page, so they’ll usually be thrilled that you’ve brought this to their attention. While it’s not guaranteed many will be more than happy to replace the link with the one you suggested (provided it’s high enough quality).
5. Conclusion
It’s important to remember that perfecting your SEO isn’t something you can do all at once. And results won’t come overnight. To keep your website ranking well, you need to keep reviewing and adapting your content.
Tools like SERanking, SEMRush or Moz can help you track exactly which keywords you are, have been, or could be ranking for. While Google Analytics and Search Console are amazing (and free!) tools that show you how much traffic certain keywords are bringing to your site. There’s so much more to Google Analytics too, which we cover a little bit on our other blog – ‘6 Things Google Analytics Can Tell You About Your Website’.
Want some advice?
Every website we develop is technically optimised for search engines, with SEO content that makes it easy for people to find you.
If you’re looking to improve your website’s SEO, drop us a line at hello@vidacreative.co.uk or give us a call at 0191 691 1293 – we’re happy to help.

